

Your veterinarian can also use single-dose ocular medications to better determine the cause of anisocoria which is referred to as pharmacological testing. The evaluation of the degree of anisocoria in dim and bright light settings allows for the diagnosis of an abnormal pupil, narrowing down the possibilities. The vet will perform a thorough ocular and neurological examination and may also recommend other tests, such as blood work or imaging, to rule out any underlying medical conditions. Oculomotor nerve lesion: This is a condition in which the oculomotor nerve (CN III), which controls the movement of the eyeball and the muscles that control pupil size, is damaged.Īnisocoria is usually diagnosed during a detailed physical examination by a veterinarian.It is usually an age-related issue and occurs commonly in senior dogs. Iris atrophy: This is a condition in which the iris (the coloured part of the eye) deteriorates.It can damage the optic nerve and lead to blindness if not treated promptly. Glaucoma: This is a condition in which the pressure inside the eye is too high.There are several conditions that can cause a dilated pupil, including:
 Corneal ulcer: An ulcer on the surface of the eye can cause enough pain to result in miosis (constriction of the pupil).ĭilated pupil (mydriasis) as the cause of anisocoria in dogs. Anterior uveitis (inflammation inside the eye): If only one eye is affected, anisocoria will be present as uveitis will result in the constriction of one pupil with the other being a normal size. This can be due to trauma, tumours, or other conditions that affect the nervous system. Horner's syndrome: A condition which is caused by damage to the sympathetic nervous system. There are a few conditions that can cause a constricted pupil, including: Constricted pupil (miosis) as the cause of anisocoria in dogs We'll look at the possible reasons based on whether the constricted or dilated pupil is the problem. There are several potential causes of anisocoria in dogs. What are the causes of anisocoria in dogs? In some cases, anisocoria can be an indication of an underlying medical condition that needs to be treated. While anisocoria is usually harmless, it is important to have any changes in pupil size evaluated by a veterinarian. Finally, certain medications and toxins can also cause the pupils to dilate or constrict. Another mechanism is the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps to keep the pupils constricted in low light conditions. The most important of these is the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the dilation and constriction of the pupils in response to light levels. There are several mechanisms that regulate pupil size in dogs. However, it is important to have anisocoria evaluated by a veterinarian, as it can sometimes be an indication of a more serious underlying condition. While it can be caused by several possibilities, in most cases it is benign and does not require treatment. What is anisocoria in dogs and what are the mechanisms that regulate pupil sizes?Īnisocoria, or unequal pupil size, is a common condition in dogs. Causes of a dilated pupil (mydriasis) include glaucoma, iris atrophy, medications and oculomotor lesion (CN III). Common causes of a smaller pupil (miosis) include Horner's syndrome, uveitis and corneal ulcer. When a dog has anisocoria, your veterinarian will determine which pupil is abnormal, the smaller or larger one. Horner syndrome is caused by interruption of the sympathetic nerves to an eye due from any cause.Anisocoria in dogs is the term used to describe a difference in the size of two pupils or uneven pupils. Horner syndrome refers to the combination of a constricted pupil, drooping eyelid, and loss of sweating around the affected eye. Disorders outside the brain that affect the sympathetic nervous system include tumors and injuries that involve the neck or upper part of the chest. Brain disorders that can affect these pathways include strokes, brain hemorrhage (spontaneous or due to head injury), and, less commonly, certain tumors or infections. Thus, people with nervous system disorders that affect the pupil often also have a drooping eyelid, double vision, and/or visibly misaligned eyes.
Corneal ulcer: An ulcer on the surface of the eye can cause enough pain to result in miosis (constriction of the pupil).ĭilated pupil (mydriasis) as the cause of anisocoria in dogs. Anterior uveitis (inflammation inside the eye): If only one eye is affected, anisocoria will be present as uveitis will result in the constriction of one pupil with the other being a normal size. This can be due to trauma, tumours, or other conditions that affect the nervous system. Horner's syndrome: A condition which is caused by damage to the sympathetic nervous system. There are a few conditions that can cause a constricted pupil, including: Constricted pupil (miosis) as the cause of anisocoria in dogs We'll look at the possible reasons based on whether the constricted or dilated pupil is the problem. There are several potential causes of anisocoria in dogs. What are the causes of anisocoria in dogs? In some cases, anisocoria can be an indication of an underlying medical condition that needs to be treated. While anisocoria is usually harmless, it is important to have any changes in pupil size evaluated by a veterinarian. Finally, certain medications and toxins can also cause the pupils to dilate or constrict. Another mechanism is the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps to keep the pupils constricted in low light conditions. The most important of these is the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the dilation and constriction of the pupils in response to light levels. There are several mechanisms that regulate pupil size in dogs. However, it is important to have anisocoria evaluated by a veterinarian, as it can sometimes be an indication of a more serious underlying condition. While it can be caused by several possibilities, in most cases it is benign and does not require treatment. What is anisocoria in dogs and what are the mechanisms that regulate pupil sizes?Īnisocoria, or unequal pupil size, is a common condition in dogs. Causes of a dilated pupil (mydriasis) include glaucoma, iris atrophy, medications and oculomotor lesion (CN III). Common causes of a smaller pupil (miosis) include Horner's syndrome, uveitis and corneal ulcer. When a dog has anisocoria, your veterinarian will determine which pupil is abnormal, the smaller or larger one. Horner syndrome is caused by interruption of the sympathetic nerves to an eye due from any cause.Anisocoria in dogs is the term used to describe a difference in the size of two pupils or uneven pupils. Horner syndrome refers to the combination of a constricted pupil, drooping eyelid, and loss of sweating around the affected eye. Disorders outside the brain that affect the sympathetic nervous system include tumors and injuries that involve the neck or upper part of the chest. Brain disorders that can affect these pathways include strokes, brain hemorrhage (spontaneous or due to head injury), and, less commonly, certain tumors or infections. Thus, people with nervous system disorders that affect the pupil often also have a drooping eyelid, double vision, and/or visibly misaligned eyes. 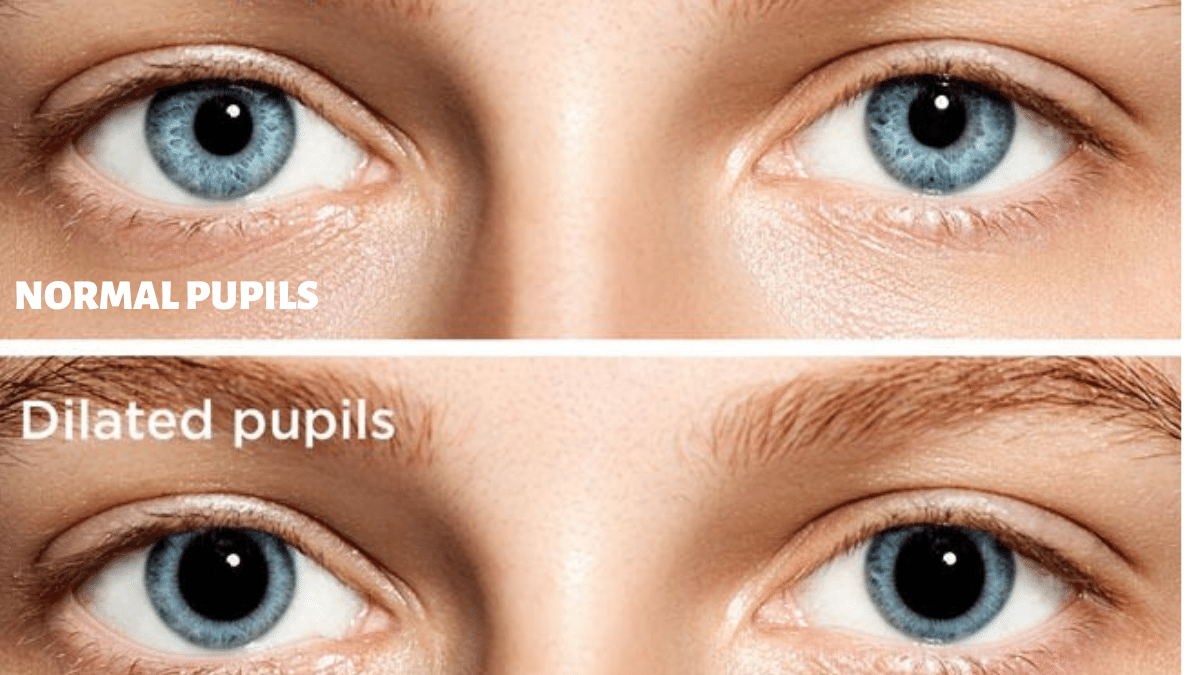

These pathways carry nerve impulses to the pupil and to the muscles that control the eye and eyelid. This system works automatically (autonomously), without a person’s conscious. Nervous system disorders that cause unequal pupils are those that affect the 3rd cranial nerve or certain parts of the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system (the autonomic nervous system Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system regulates certain body processes, such as blood pressure and the rate of breathing.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
